In today’s fast-paced world, maintaining brain sharpness and heart health is more important than ever. One powerful nutrient that plays a crucial role in both cognitive function and cardiovascular well-being is Omega-3 fatty acids. These essential fats, found in foods like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, are widely known for their ability to enhance brain function, improve memory, and support heart health.
Scientific research has shown that Omega-3s help reduce inflammation, lower bad cholesterol, and support healthy blood circulation, all of which contribute to a stronger heart. Additionally, they play a vital role in brain development, mental clarity, and even mood regulation, making them essential for people of all ages.
In this article, we will explore how Omega-3 fatty acids benefit both the brain and the heart, the best sources to include in your diet, and how you can optimize their intake for long-term health.
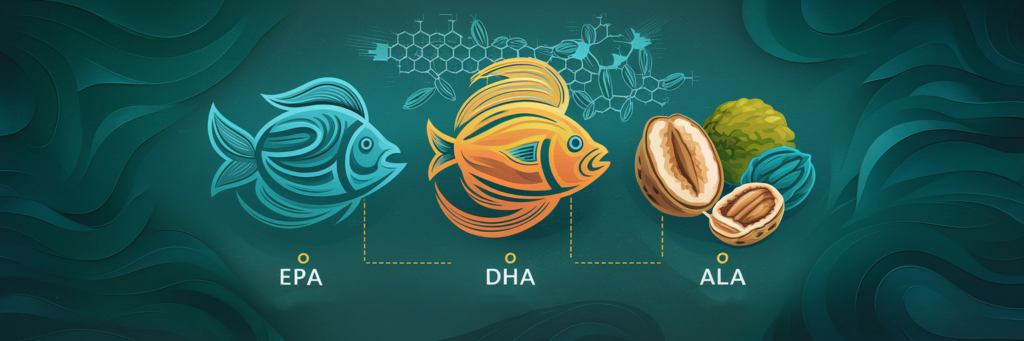
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are a group of essential fats that play a vital role in maintaining overall health. Since our bodies cannot produce Omega-3s on their own, they must be obtained through diet or supplements. These fatty acids are crucial for brain function, heart health, and reducing inflammation.
Types of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
There are three main types of Omega-3s, each with unique benefits:
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid)
- Primarily found in fatty fish.
- Plays a key role in reducing inflammation and improving cardiovascular health.
- Helps manage mental health conditions like depression and anxiety.
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid)
- The most important Omega-3 for brain function and development.
- Essential for memory, learning, and cognitive performance.
- Found in high concentrations in the brain and retina, making it critical for vision and neurological health.
- ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid)
- Found in plant-based sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
- The body converts ALA into EPA and DHA, but in small amounts.
- Important for vegetarians and vegans who may need to rely on plant-based Omega-3 sources.
Best Dietary Sources of Omega-3s
To ensure adequate Omega-3 intake, include these foods in your diet:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, tuna, herring.
- Plant-Based Sources: Flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, walnuts.
- Seafood & Algae: Seaweed, algae-based Omega-3 supplements.
- Enriched Foods: Omega-3 fortified eggs, dairy, and certain oils.
By incorporating these nutrient-rich foods, you can naturally boost your Omega-3 levels and support your brain and heart health.
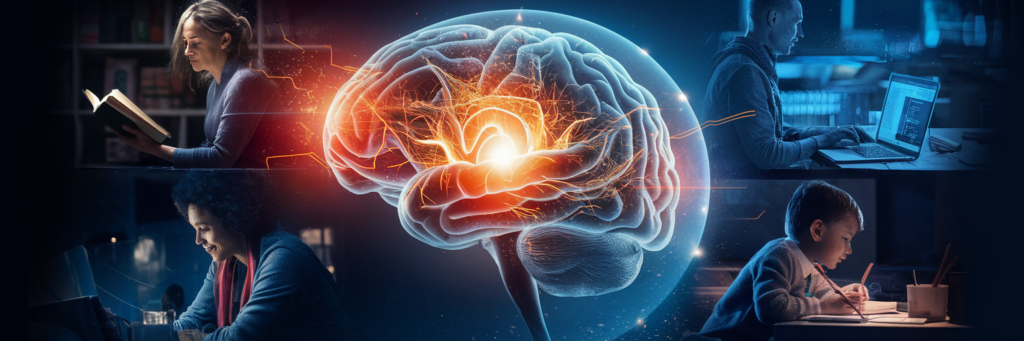
Omega-3 and Brain Health
The brain is made up of nearly 60% fat, and DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid)—one of the primary Omega-3 fatty acids—is a key structural component of brain cells. This makes Omega-3s essential for maintaining cognitive function, supporting mental health, and reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
1. Cognitive Function and Memory
- DHA helps maintain brain cell membranes, promoting efficient communication between neurons.
- Studies show that Omega-3s improve memory, focus, and learning abilities.
- Regular intake is linked to better problem-solving skills and mental sharpness.
2. Mental Health Benefits
- Omega-3s, particularly EPA, have been found to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- They help regulate neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, which influence mood.
- Low Omega-3 levels are often associated with higher risks of mood disorders.
3. Omega-3s and Aging: Protecting Against Dementia and Alzheimer’s
- As people age, brain function naturally declines, increasing the risk of Alzheimer’s and dementia.
- Omega-3s help reduce brain inflammation and prevent cognitive decline.
- Some studies suggest that Omega-3 intake may help delay the onset of memory-related disorders.
4. Omega-3s for Children and Pregnancy
- During pregnancy, DHA is critical for fetal brain development.
- Children with sufficient Omega-3 intake tend to have better attention spans, cognitive function, and behavioral health.
- Omega-3 supplementation has shown benefits for ADHD management, improving focus and impulse control.
The Bottom Line
Regular consumption of Omega-3 fatty acids nourishes the brain, enhances mental clarity, and supports emotional well-being. Whether through diet or supplements, ensuring a steady intake of these essential fats can have long-term cognitive benefits.

Omega-3 and Heart Health
Omega-3 fatty acids are well known for their powerful heart-protective benefits. Research has consistently shown that these essential fats help reduce the risk of heart disease, lower cholesterol levels, and improve overall cardiovascular function.
1. Reduces Inflammation
- Chronic inflammation is a major factor in heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure.
- Omega-3s, especially EPA, have anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce inflammation in blood vessels, promoting better heart health.
2. Lowers Triglycerides and Balances Cholesterol
- High triglyceride levels are linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
- Omega-3s help reduce triglyceride levels by up to 30%.
- They also increase “good” HDL cholesterol while helping to lower “bad” LDL cholesterol.
3. Prevents Blood Clots and Stroke
- Omega-3s make blood less likely to clot, reducing the risk of dangerous blockages in arteries.
- This lowers the chances of stroke, heart attack, and other cardiovascular complications.
4. Supports Healthy Blood Pressure
- Studies have found that Omega-3s help lower blood pressure, especially in people with hypertension.
- They relax blood vessels, improving circulation and reducing strain on the heart.
5. Regulates Heart Rhythm and Reduces Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death
- Omega-3s help maintain a stable heart rhythm, reducing the risk of arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats).
- This is particularly important for individuals with a history of heart disease.
- Regular intake has been linked to a lower risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
The Bottom Line
Omega-3 fatty acids are one of the most effective natural nutrients for heart health. Whether from fatty fish, plant-based sources, or supplements, incorporating Omega-3s into your diet can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and improve overall heart function.

Best Ways to Incorporate Omega-3 in Your Diet
To fully benefit from Omega-3 fatty acids, it’s essential to include the right foods in your daily meals. While supplements can be helpful, the best way to get Omega-3s is through a balanced diet rich in natural sources.
1. Omega-3 Rich Foods
Here are the best food sources for each type of Omega-3:
Animal-Based Sources (High in EPA & DHA)
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, tuna, herring.
- Shellfish: Oysters, shrimp.
- Omega-3 Enriched Eggs: These come from hens fed an Omega-3-rich diet.
Plant-Based Sources (High in ALA)
- Flaxseeds (and flaxseed oil)
- Chia seeds
- Walnuts
- Hemp seeds
- Algae & Seaweed (A great DHA source for vegetarians/vegans)
2. Omega-3 Supplements
If your diet lacks enough Omega-3s, supplements can help:
- Fish Oil: The most common supplement, rich in both EPA and DHA.
- Krill Oil: A high-quality alternative with added antioxidants.
- Algal Oil: The best plant-based source of DHA, ideal for vegetarians and vegans.
💡 Tip: When choosing supplements, look for high-quality, mercury-free options with proper certifications.
3. Cooking with Omega-3s
- Use flaxseed oil in smoothies or salads (avoid heating it).
- Add chia seeds to oatmeal, yogurt, or baked goods.
- Include walnuts in snacks, salads, or cereal.
- Grill or bake fatty fish for a heart-healthy meal.
The Bottom Line
A diet rich in Omega-3s can be easily achieved by consuming a variety of fatty fish, nuts, seeds, and healthy oils. Supplements can also be a good option, especially for those who don’t eat fish.

Potential Risks & Considerations
While Omega-3 fatty acids offer numerous health benefits, it is important to be aware of potential risks and considerations associated with their consumption. Overconsumption or poor-quality sources may lead to unwanted side effects.
1. Possible Side Effects of Omega-3s
- Fishy Aftertaste or Burps: Common with fish oil supplements, but can be minimized by taking them with meals or choosing enteric-coated capsules.
- Digestive Issues: Some individuals may experience bloating, nausea, or diarrhea, especially when taking high doses.
- Allergic Reactions: Those with seafood allergies should opt for plant-based sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, or algal oil.
2. Blood-Thinning Effects
- Omega-3s have a natural blood-thinning property, which can be beneficial for heart health but may increase bleeding risk in certain cases.
- People taking blood thinners (such as aspirin or warfarin) should consult a doctor before increasing Omega-3 intake.
3. Risk of Contaminants in Fish & Supplements
- Some large fish (like swordfish and king mackerel) may contain high levels of mercury, which can be harmful, particularly for pregnant women.
- Always choose high-quality, purified fish oil supplements that are tested for mercury and other contaminants.
4. Omega-3 Overdose & Imbalance
- While Omega-3s are beneficial, excessive intake (above 3,000 mg per day) may cause:
- Excessive bleeding or bruising.
- A weakened immune system.
- Potential blood sugar spikes in diabetics.
- It is best to follow recommended daily dosages based on age and health needs.
The Bottom Line
Omega-3s are generally safe and beneficial, but moderation is key. Choosing high-quality sources and balancing intake with other healthy fats ensures you reap the benefits without unwanted side effects. If you have medical conditions or take medication, consult a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes.

Conclusion
Omega-3 fatty acids are among the most important nutrients for maintaining both brain and heart health. From boosting cognitive function and memory to reducing the risk of heart disease, these essential fats play a crucial role in overall well-being.
By incorporating Omega-3-rich foods such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, or by taking high-quality supplements, you can ensure that your body gets the necessary amounts of EPA, DHA, and ALA. Whether you are looking to enhance mental clarity, lower cholesterol, or prevent inflammation, Omega-3s offer a natural and effective way to support long-term health.
However, it’s important to consume Omega-3s in moderation and choose high-quality sources to avoid potential risks. If you have existing health conditions or are on medication, consult a healthcare professional before making major dietary changes.
Incorporating Omega-3s into your daily routine is a simple yet powerful step toward a healthier brain, a stronger heart, and a better quality of life. Start today and experience the benefits of this super-nutrient for yourself!



